OUR SOLUTIONS
GWASmeRNA™
Prioritize Functional GWAS Variants Through RNA Methylation and Tissue-Specific Insights
PROBLEM
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have uncovered thousands of SNPs linked to human diseases, but the vast majority lie in noncoding regions, making it challenging to interpret their functional impact.
Traditional post-GWAS analyses typically focus on DNA-level features—such as transcription factor binding sites and enhancers— or eQTL studies linking variants to gene expression but often overlook RNA-level regulatory mechanisms. It's important to recognize that
up to 85% of the human genome is transcribed into RNA, and recent studies have shown a significant enrichment of GWAS SNPs in m⁶A-modified RNA regions. This suggests that RNA methylation may play a key role in mediating the effects of disease-associated variants, yet it remains underexplored in current SNP prioritization pipelines.
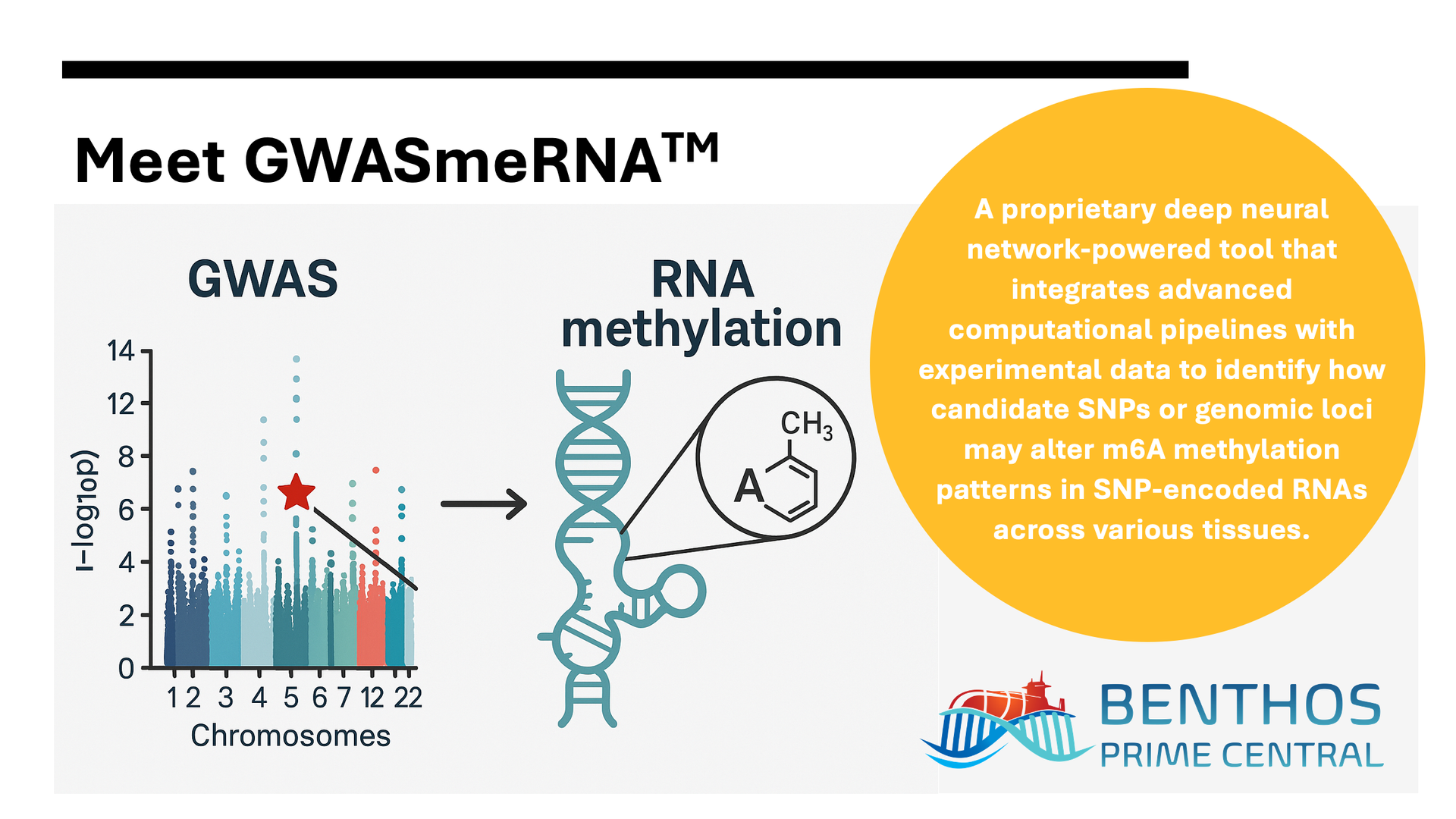
OUR SOLUTION
To help fill this critical gap in post-GWAS functional analysis, we’ve developed GWASmeRNA™ — a deep neural network–powered tool that predicts how your candidate SNPs or genomic regions of interest may alter
m6A methylation patterns in SNP-encoded RNAs across tissues. This enables functional prioritization of variants and reveals
mechanisms beyond association signals.
Are you interested in any of the following?
- Do you have a GWAS locus or SNP associated with a trait whose functional impact is unknown?
- Are there genomic regions you’d like to explore for a potential link to RNA methylation and post-transcriptional regulation?
- Do you want to prioritize candidate SNPs by understanding their potential effect on m⁶A RNA methylation patterns across tissues?
What we need from you?
- List of SNPs or genomics regions of your interest
- Genomic region coordinates with reference genome build
What will we deliver?
- Map of m6A RNA methylation motifs in your SNP-associated genomic regions
- Predicted m6A RNA methylation scores for both reference and variant alleles, their comparison, revealing how a SNP may alter methylation potential.
- Tissue-specific m6A RNA methylation of your SNP-associated genomic regions across >30 human/mouse tissues
